Grahan: Solar and Lunar Eclipses in Hindu Culture and Beyond
Introduction:

Amid a vast array of celestial phenomena, the enigmatic phenomenon of Grahan, encompassing both solar and lunar eclipses, emerges as an enthralling enigma. The spectacle of a solar eclipse unfolds when the moon veils the radiant countenance of the sun, casting its shadow upon the Earth and briefly obscuring the sun’s luminosity. Conversely, the occurrence of a lunar eclipse takes shape as the Earth positions itself between the sun and the moon, projecting a shadow that graces the moon with a captivating array of copper tones. These infrequent junctures, wherein cosmic entities achieve perfect alignment, have persistently bewildered and enchanted humanity across epochs.
The allure exerted by Grahan extends well beyond its celestial mechanics, permeating the very core of human existence. Solar and lunar eclipses have, across diverse cultural landscapes, ignited profound contemplation regarding the spiritual domain, frequently construed as celestial clashes or potent symbols of transformation and transition. Intertwined within these phenomena are cultural narratives, wherein societies have woven myths and rituals to commemorate these momentous occurrences.
Understanding Solar and Lunar Eclipses:
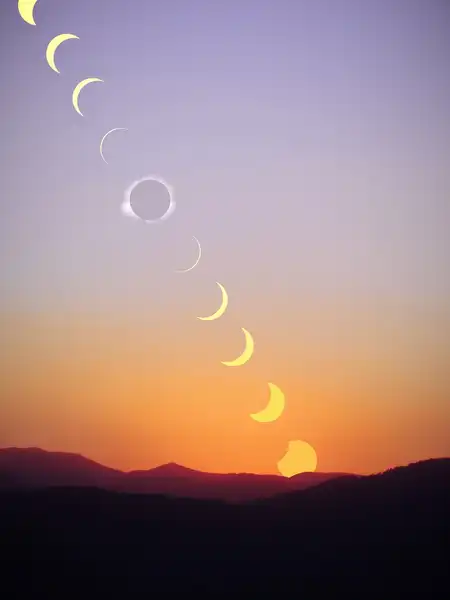

Solar and lunar eclipses, captivating in their celestial grandeur, arise from the intricate gravitational choreography involving the Earth, the moon, and the sun. A solar eclipse materializes when the moon strategically interposes itself between Earth and the sun, casting an evocative shadow over our planet. This celestial alignment orchestrates the partial or complete obscuration of the sun’s luminous emanations, culminating in a riveting spectacle that graces the diurnal canvas. In contrast, the unfolding of a lunar eclipse transpires as Earth adroitly maneuvers its position between the sun and the moon. The Earth’s shadow enshrouds the moon, inducing a captivating transformation wherein the once effulgent lunar orb takes on a distinctive reddish hue.
Pivotal disparities delineate solar and lunar eclipses on several salient dimensions. Primarily, the axis of alignment: a solar eclipse mandates the meticulous alignment of the sun, moon, and Earth along a direct linear trajectory, whereas a lunar eclipse involves a subtly angled configuration. Secondly, the facet of visibility: solar eclipses manifest within a delimited geographical region acknowledged as the path of totality, while lunar eclipses unveil themselves from any nocturnal vantage point on Earth’s hemisphere.
These two archetypal celestial events also diverge in terms of their visual impact: a solar eclipse begets ephemeral darkness as the moon’s shadow sweeps across Earth’s expanse, while a lunar eclipse swathes the moon in a captivating radiance reminiscent of burnished copper, owing to the refraction and diffraction of sunlight by Earth’s atmospheric constituents.
Grahan, whether solar or lunar in manifestation, remain extraordinary occurrences due to their infrequent frequency and unforeseeable emergence. While their incidence adheres to discernible patterns governed by the consistent orbital mechanics of the moon and Earth, the meticulous alignment indispensable for an eclipse represents a delicate cosmic ballet, unfolding merely a handful of times annually.
Furthermore, the observability of these celestial phenomena experiences fluctuations contingent upon geographical coordinates and prevailing atmospheric conditions, thereby infusing an element of capriciousness into the act of witnessing them. The inherently unpredictable nature of eclipses has historically engendered a blend of astonishment and conjecture within diverse global cultures, catalyzing the creation of a diverse spectrum of myths and rituals, all of which are devised to illuminate and reverentially acknowledge these entrancing occurrences.
Grahan in Hindu Culture:
Nestled intricately within the intricate weave of Hinduism, the celestial pageantry of eclipses, denoted as Grahan, resounds with a profoundly resonant spiritual tenor, intricately enmeshed in the very fabric of religious ardor. The harmonious choreography enacted by the sun, moon, and Earth during these celestial occurrences mirrors the intricate ballet of energies that course through both the universe and the human spirit. Operating as a celestial conduit, this phenomenon propels individuals towards elevated spiritual plateaus, fostering the unfurling of meditative profundities, introspection, and communion with the divine that extends well beyond the bounds of the mundane plane.
Grahan, whether they materialize as solar or lunar in nature, are apprehended within the sphere of Hinduism as epochs suffused with heightened energy and spiritual potency. This spiritual ethos perceives these junctures as moments when the veils demarcating the material and spiritual dimensions are particularly tenuous, extending an open invitation to devotees for immersive meditation, supplication, and contemplation. The convergence of cosmic forces during an eclipse is surmised to augment the impact of these spiritual practices, thereby facilitating a more profound interlacing with the inner self and the cosmic consciousness.
An eminent ritual intricately intertwined with eclipses within the Hindu spiritual ethos is the temporary shuttering of temples. This practice emanates from the deep-seated conviction that during an eclipse, disturbances in the Earth’s energy field might impinge upon the sanctity both of the corporeal and the ethereal realms. Consequently, temples are temporarily sealed to thwart the intrusion of impurities and to fashion a dedicated space conducive to unwavering meditation and prayer during this potent cosmic juncture. The spiritual ceremonies embarked upon during the eclipse are believed to cleanse the self and the environment, harmonizing individuals with heightened frequencies and facilitating a profound union with the very quintessence of the divine.
Myths and Beliefs about Grahan:
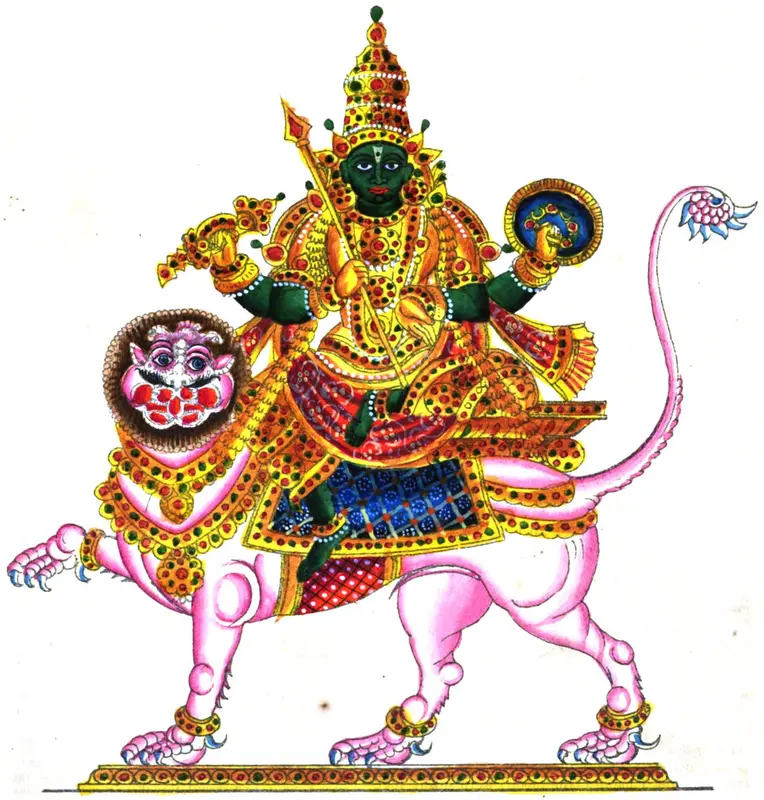

Enveloping the celestial phenomenon of Grahan is a tapestry of enchanting narratives woven intricately within Hindu mythology. Among these captivating chronicles, one tale unfurls the saga of Rahu, a shrewd demon who artfully deceived the gods to partake of the elixir of immortality. In the wake of Rahu’s cunning exposure, Lord Vishnu acted with celerity, severing his head and giving rise to both Rahu and his corporeal counterpart, Ketu. In a ceaseless pursuit, Rahu and Ketu relentlessly trail the sun and moon through the firmament, intermittently overtaking them during eclipses, symbolizing their ephemeral dominance over the celestial luminaries.
Nurtured within Hindu mythology, the genesis of eclipses emerges from the cosmic churn known as the Samudra Manthan. This fervent quest for the elixir of perpetual life led the deities and demons to stir the cosmic ocean, unveiling the sun and moon as resplendent treasures. Eclipses unfurl as the asuras, or demons, seek to engulf these celestial gems, briefly causing their vanishing. Stepping in, the divine beings, under Lord Vishnu’s watch, intervene to safeguard the radiant entities, encapsulating the perpetual struggle between enlightenment and obscurity, sagacity and ignorance.
These mythic narratives sculpt the cultural convictions and practices surrounding eclipses in profound ways within Hinduism. The chronicle of Rahu and Ketu imparts a profound understanding of the karmic reverberations entwined with deceit and avarice, serving as a moral lesson highlighting the hazards posed by self-serving endeavors. The saga of the Samudra Manthan underscores the cyclic rhythm intrinsic to existence, with eclipses prompting reflection on the balance maintained amidst opposing cosmic dynamics. As a result, eclipses usher in moments of deep introspection and spiritual rejuvenation.
Cultural observances during eclipses resonate with the resonance of these age-old legends. Temples are momentarily sealed to guard against impurities and foster inner contemplation. Devotees embrace meditation, prayer, and fasting to cleanse themselves both spiritually and energetically. Eclipses are regarded as inauspicious junctures for initiating new ventures, underscoring the belief in the cyclical cadence that underpins life’s myriad facets.
Grahan Rituals and Practices:
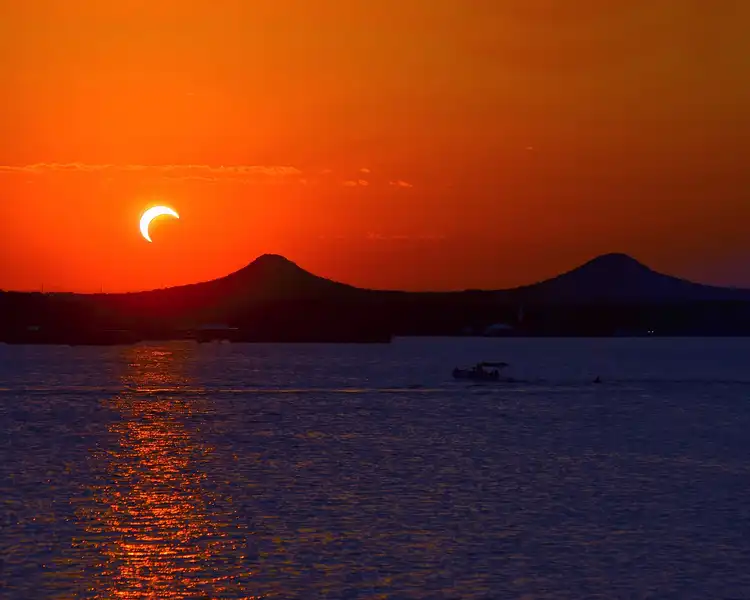

The celestial phenomenon of Grahan, encompassing the occurrence of eclipses, holds a significant realm within the Hindu tradition, giving rise to an array of rituals and practices that chart a course toward spiritual purification and revitalization. Rooted in timeless wisdom, these observances underscore the profound imperative of harmonizing one’s inner essence with the rhythm of the cosmos during these exceptional celestial junctures.
Amidst a Grahan, adherents of Hinduism partake in a series of rituals that have been meticulously fashioned to cleanse both the physical and spiritual dimensions. Amidst these practices, a pivotal ritual is the act of ritual bathing, wherein individuals immerse themselves in consecrated rivers or waters before and after the eclipse. This symbolic purification is believed to absolve individuals of malevolent energies and impurities, thereby paving the path toward a rekindled spiritual alignment.
The tradition of fasting during eclipses is widely observed, grounded in the notion that it heightens one’s receptivity to cosmic forces and transcendental insights. Through voluntary abstention from sustenance and physical indulgence, practitioners create a conducive backdrop for introspection and meditation. Concurrently, the vocalization of mantras – sacred phonetic utterances – forms an integral component of eclipse rituals. The resonant vibrations of these mantras are perceived to attune the participant to elevated frequencies, thereby enabling a more profound communion with the divine.
The rituals intertwined with Grahan bear profound symbolic significance. The ritual of ablution metaphorically signifies the obliteration of transgressions and adverse influences, thus clearing the path for spiritual rejuvenation. Fasting functions as a means to restrain sensory impulses, quieting corporeal desires and allowing the intellect to turn inward. The recitation of mantras channels affirmative vibrations, refining the psyche and harmonizing an individual’s vitality with the pulsations of the cosmic continuum.
Significance of Grahan Other Cultures:

Grahan, those transcendent cosmic events, have artfully woven a captivating mosaic of beliefs and practices across a diverse spectrum of world cultures. From the earliest epochs of antiquity to the intricate tapestry of the contemporary era, these celestial occurrences have ignited profound human fascination, interweaving threads of connection among disparate societies through a shared sense of awe and reverence.
In antiquity, eclipses often stirred a range of emotions, encompassing awe, trepidation, and a deep impetus for spiritual contemplation. In the annals of Mesopotamia, cuneiform tablets meticulously recorded eclipses as portents heralding royal destinies or serving as celestial messages. In the cultural landscape of China, the imagery of celestial dragons consuming the sun or moon gave rise to rituals involving clamorous noise-making to ward off these mythical entities. Amid the Maya civilization, eclipses became inseparably linked with divine manifestations, leading to meticulous documentation of their temporal occurrences, for purposes both of astronomical precision and religious devotion. Native American cultures, on occasion, infused eclipses with symbolic weight, interpreting them as cosmic confrontations of deities.
Amid this kaleidoscope of interpretations, certain core themes and rituals transcended the boundaries of cultural distinctions. Eclipses frequently acted as catalysts for heightened spiritual observances, meditative rituals, and offerings designed to placate the cosmic forces. A recurrent motif was the perception of eclipses as thresholds of transition, delineating the liminal realm between light and shadow, mortality and transcendence, the mundane and the ethereal. The temporary suspension of the natural order during an eclipse was often believed to hold both latent dangers and transformative potentials.
The allure of Grahan, stemming from the shared human yearning for celestial contemplation, has fostered interconnections across cultures throughout the chronicles of history. These cosmic phenomena were meticulously observed and decoded by a spectrum of societies, each infusing them with distinct cultural hues and mythologies. The rich diversity in eclipse beliefs and practices serves as a vivid testament to the multifaceted tapestry of human creativity, revealing the myriad ways in which diverse cultures endeavored to apprehend and interact with the enigmatic realm of the cosmos.
Grahan and Modern Society:
Even in the contemporary age, as our extensive scientific comprehension gradually unveils the intricate mechanics behind eclipses, humanity’s captivation with these cosmic phenomena remains resolute. Eclipses endure as enthralling events, effectively bridging the divide between rational understanding and mystical allure, scientific exploration, and spiritual reverence.
In today’s context, the phenomenon of Grahan, encompassing eclipses, is observed through the twin prisms of culture and science. From a cultural vantage point, diverse societies worldwide still ascribe profound significance to eclipses, often echoing ancient beliefs and rituals. Temples may temporarily close their doors, ceremonial observances may unfold, and gatherings may convene to pay homage to these celestial occurrences. These practices serve as a manifestation of an enduring cultural heritage and a profound connection between humanity and the celestial realm.
Eclipses, as they have done for generations, continue to foster a sense of unity among people through shared anticipation and wonder. The allure of observing a solar eclipse, momentarily shrouding the day in nocturnal shades, or a lunar eclipse, adorning the moon in captivating coppery hues, transcends cultural and geographical confines. The enduring allure of eclipses in the modern world underscores the concept that, despite technological progress, our interconnectedness thrives through an inherent fascination with the vast expanse of the universe.
Cultural Traditions and Adaptations:

The traditions surrounding Grahan have undergone a captivating metamorphosis, shaped by the currents of time, cultural evolution, and scientific progress. Ancient practices, deeply rooted in myth and conviction, have now harmonized with the principles of modern science and the interconnected global society, resulting in a delicate equilibrium between heritage and contemporary understanding.
In the context of today’s interconnected world, Grahan is embraced with a harmonious fusion of tradition and innovation. While the fundamental beliefs and rituals remain unchanged, their expression has evolved. Temples may still observe temporary closures, yet there is an increasing emphasis on public education, shedding light on the scientific foundations that underlie eclipses. Individuals engage with Grahan in a manner that blends their cultural heritage with a deeper comprehension of the universe.
Curious individuals seeking meaningful participation have a wealth of resources at their disposal. Scientific institutions, cultural organizations, and spiritual communities often offer information about upcoming eclipses, accompanied by insights into cultural traditions and contemporary interpretations. These resources empower individuals to engage in ways that resonate with their personal convictions, all while recognizing the intricate historical and cultural tapestry woven by the phenomenon of Grahan.
Grahan Symbolism and Personal Growth:

Grahan, with its ethereal interplay of shadows and luminosity, bears profound symbolism as a harbinger of change, metamorphosis, and profound introspection. Much like the transient dimming of the sun and moon, eclipses symbolize a momentary veiling of clarity, inviting us to delve into the depths of our essence, reconsider our paths, and emerge with revitalized perspectives.
Eclipses offer potent opportunities for inner evolution and rejuvenation. Amidst the hustle and bustle of daily life, these cosmic events provide a window for introspection. The darkening of celestial bodies can be viewed as an invitation to temporarily eclipse external distractions and engage in deep self-contemplation. Within this stillness, we have the opportunity to unearth hidden truths and embark on journeys of self-discovery.
The spiritual dimensions of Grahan seamlessly intertwine with the realms of personal growth. Much like an eclipse’s fleeting shadow, personal development entails confronting our inner shadows—the doubts, fears, and limitations. Just as the sun emerges from behind the moon’s cover, we can emerge from moments of introspection with heightened clarity and renewed purpose.
Ancient eclipse rituals, marked by purification, fasting, and meditation, align harmoniously with modern methodologies of personal growth. Purification practices mirror the shedding of outdated patterns, fasting fosters discipline and mindfulness, and meditation nurtures inner serenity and insight. By embracing these practices during an eclipse, we meld age-old wisdom with contemporary techniques for self-improvement.
Conclusion:
Grahan, the celestial spectacle of eclipses, intricately weaves together a complex mosaic that encompasses the realms of spirituality, science, and culture. Its significance is multifaceted: spiritually, it embodies transformation and introspection; scientifically, it emerges from precisely choreographed cosmic alignments. Across diverse cultures and societies, Grahan has sparked rituals and beliefs that pay homage to its celestial ballet.
In cultures around the world, Grahan carries profound spiritual significance. Ancient myths and rituals interlace eclipses with celestial struggles and divine messages. Temples close their doors, individuals engage in meditative practices, and communities gather to honor these celestial occurrences. These practices, steeped in history, serve as a testament to humanity’s enduring connection to the universe and its mysteries.
I aspire for this article to provide you with assistance. Should you discover value within these words, kindly contemplate sharing them with your loved ones. I invite you to spare a moment to offer your thoughts and appraisals below. For further remarkable content akin to this, I encourage you to delve into our website. Additionally, I extend an invitation to subscribe to my YouTube channel for forthcoming materials of similar nature. Lastly, feel unrestrained to establish a connection with me through social media. Wishing you a splendid day ahead!
हरि ॐ तत्सत्
FAQs:
Here are a few frequently asked questions (FAQs) regarding the Grahan: